Acute mouth problems.

Which of the following statements is UNTRUE about tongue lacerations?
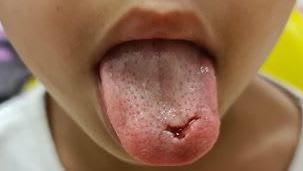
The tongue has an excellent blood supply so often heals well but through and through lacerations generally do require repair.
Importantly when aspirating a quinsy (peritonsillar abscess) where is the internal carotid artery in relation to the tonsil?
As a result make sure you sheath your aspiration needle so that only about 1cm can enter the tonsil.
This lady has tongue swelling from angioedema caused by an ACE inhibitor. Which therapies would be the best combination to use to treat her?

ACE inhibitor angioedema does not respond to adrenaline, steroids and anti histamines---the mainstay of treatment in anaphylaxis.
ACEi angioedema responds differently to Hereditary angioedema but tranexamic acid and FFP is a reasonable and easily available option.
EMcrit does a good review. https://emcrit.org/ibcc/angioedema/#bradykinin_angioedema:_treatment
Fortunately we have a vaccine to the bacterial infection Diphtheria (the D in DPT vaccine). Which of the following statements is NOT true?
Unvaccinated children still occasionally get Diphtheria. There were 2 cases in NSW in July 2022.
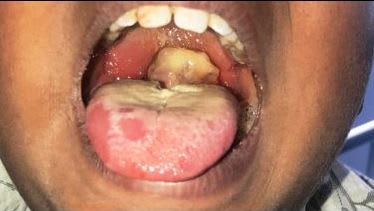
Which of these celebrities suffered from carcinoma of the tongue?
Michael Douglas developed tongue carcinoma from HPV (Human Papilloma Virus).
This is a photo of "Black Hairy Tongue". Which of the following is associated with it occurring?
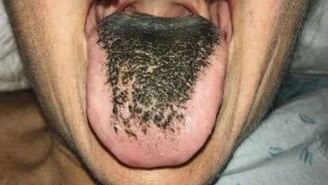
The papillae become enlarged and change colour to black, giving the appearance of a black hairy tongue.
Which of the following is NOT TRUE about Strep pharyngitis?
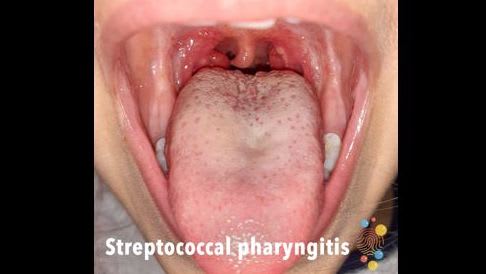
Penicillin is still the mainstay of the treatment of proven Strep pharyngitis. Treatment is especially important in the Indigenous population to help decrease acute rheumatic fever. In the NT the incidence of acute rheumatic fever is the highest in the world.
This child developed these painful lesions following a brief prodrome of fever and anorexia. What do you think it is?
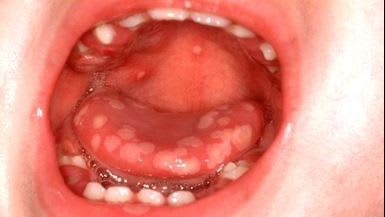
Generally the child's problem is oral pain with refusal to drink. Most of the time it self limits in 10 to 14 days ard only requires supportive treatment with simple oral analgesia and Xylocaine viscus to assist. In immunocompromised patients IV antivirals may be required.
Which of the following IS part of the accepted treatment of post tonsillectomy bleed?
I would suggest gargle 3% Hydrogen Peroxide diluted i in 3 with iced water. Sit the patient up. Bilateral compression of Carotid arteries is a very unwise idea.
What best describes the 2 hand relocation technique for a bilateral dislocation of the temporomandibular joint?
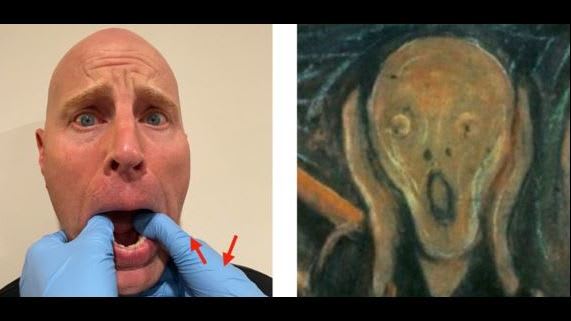
This traditional technique usually requires some cautious sedation. Having the patient sitting upright in a bed and a second operator holding the forehead whilst the relocation occurs assists, otherwise the head comes forward with the operator.
Other techniques that require less sedation include the "syringe technique". Here is a link explaining some other techniques.
https://sinaiem.org/foam/4-reduction-techniques-of-anterior-mandible-dislocation/